Mississippi
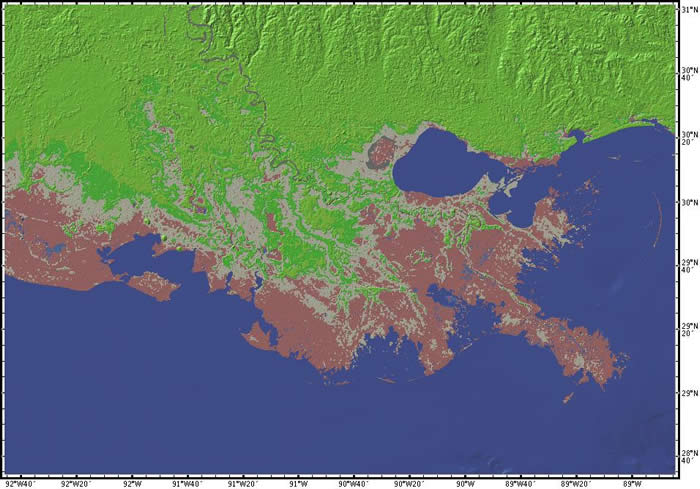
Location: Delta of the Mississippi River, Louisiana, USA
Latitude: 30° N
Longitude: 91° W
Image Width: 390 km (240 miles)
Data: Shipboard multibeam bathymetry data (ocean), Shuttle Radar Topographic Mission (SRTM) (land)
Description: The Mississippi River, the largest river in North America, loses velocity and divides into 'distributaries' as it meets the Gulf of Mexico. Sediment from much of central North America is deposited in an expanding fan-shaped delta. The accumulation of sediment is ever-changing, and the Mississippi's primary channel shifts frequently in the delta region. The surrounding areas consist of coastal mudflats, marshes, and tidal pools. |
|
Monterey Bay
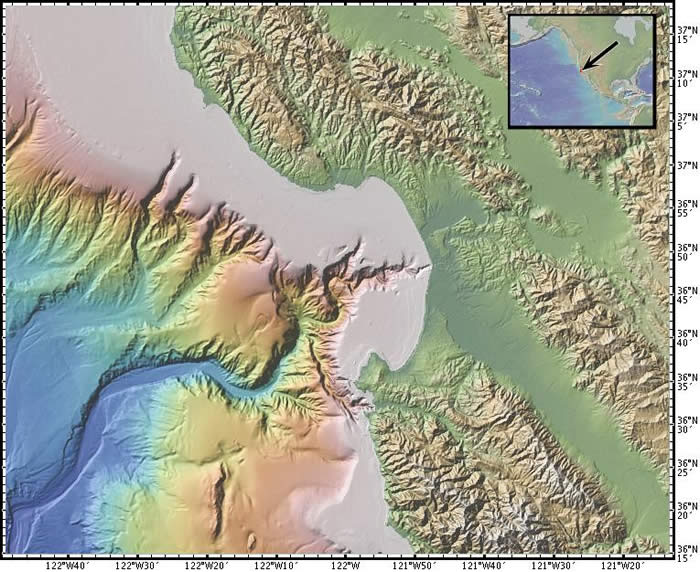
Location: Monterey Bay and Monterey Canyon, California, USA
Latitude: 37° N
Longitude: 122° W
Image Width: 150 km (90 miles)
Data: Shipboard multibeam bathymetry data (ocean), Shuttle Radar Topographic Mission (SRTM) (land)
Description: This image shows the land and ocean areas around Monterey Bay, just south of San Francisco, CA. The city of Santa Cruz is on the northern shore of the bay. The city of Monterey is on the southern side; the Big Sur coast extends southward.
Because this area is part of the convergent plate boundary between the Pacific plate to the west and the North American plate to the east, many geologic faults cross the area of the image. The San Andreas fault runs through the easternmost valley shown here.
This bay is one of the most biologically diverse bodies of water in the world, and the underlying submarine canyon is one of the deepest underwater canyons along the continental United States. Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute (MBARI) is located in Moss Landing, midway along the bayshore, where its two research ships and remotely operated vehicles are berthed, giving them immediate access to Monterey Bay.
The ocean area shown in this image is part of Monterey Bay National Marine Sanctuary (MBNMS) a Federally protected marine area offshore of California's central coast. Stretching from Marin to Cambria, the MBNMS encompasses a shoreline length of 276 miles and 5,322 square miles of ocean. Supporting one of the world's most diverse marine ecosystems, it is home to numerous mammals, seabirds, fishes, invertebrates and plants in a remarkably productive coastal environment. |
|
Gulf of California
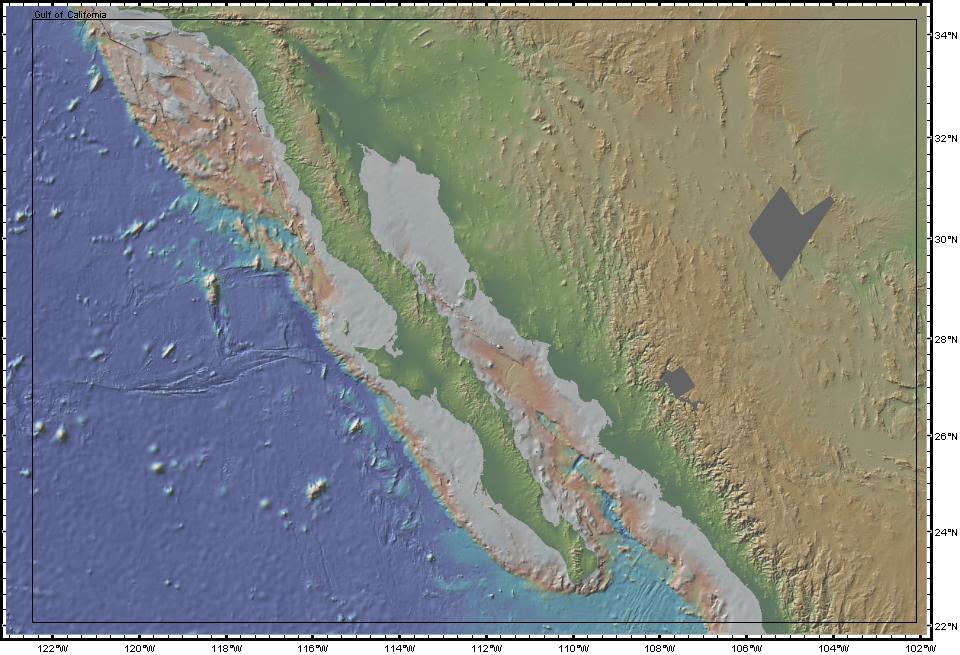
Location: Baja California, Mexico and the Gulf of California
Latitude: 23° to 32° N
Longitude: 106° to 116° W
Image Width: 600 km (900 miles)
Data: Shipboard multibeam bathymetry data (ocean), Shuttle Radar Topographic Mission (SRTM) (land)
Description: This view shows the Pacific ocean, the Baja California peninsula, the Gulf of California and a portion of the west coast of Mexico. Gray areas indicate no data.
The San Andreas fault system continues into the Gulf of California as the major boundary zone between the Pacific and North America plates. Across this boundary, extension and strike-slip faulting is causing the Baja California peninsula to move away from mainland of Mexico, thereby opening the Gulf of California.
The 3D view is looking north-westward along the axis of the Gulf. |
|
Nantucket Sound
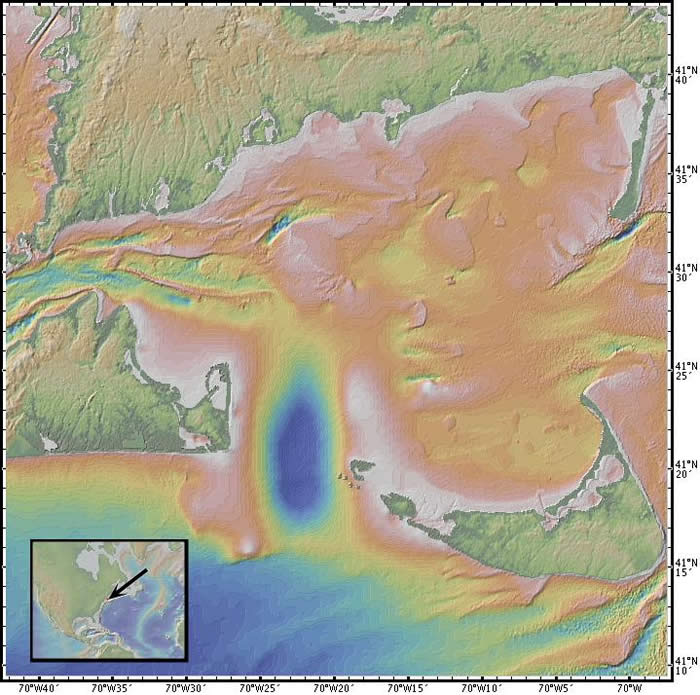
Location: southern side of Cape Cod, Massachusetts, USA
Latitude: 41° 30' N
Longitude: 70° 20' W
Image Width: 63 km (40 miles)
Data: Shipboard multibeam bathymetry data (ocean), Shuttle Radar Topographic Mission (SRTM) (land)
Description: This view shows the southern side of Cape Cod, from Woods Hole on the left to Chatham on the right. The islands of Martha's Vineyard (left) and Nantucket (right) are separated by the deep water (blue) of the Muskeget channel. Shifting sandbars show up clearly in this image.
An offshore wind farm of wind-driven electricity-producing windmills has been proposed for Horseshoe Shoals, the shallow (brown-white) area north of the Muskeget channel.
The landforms in this image show the effects of glaciation; a terminal moraine can be traced across both Martha's Vineyard and Nantucket Island. |
|